Direct materials procurement is at the core of manufacturing, as it impacts cost structures, product quality, and delivery performance. Manufacturers confront growing pressure to optimize their sourcing strategies while negotiating complicated issues such as supply chain interruptions, environmental concerns, and ethical considerations. At Source One, we know that a well-executed sourcing strategy is not only about procurement; it can also generate innovation, resilience, and provide a competitive edge.
Best Practices for Direct Materials Sourcing
Based on our industry expertise, we’ve discovered numerous best practices that manufacturers may use to maximize their direct materials sourcing strategies.
Develop Clear Policies and Codes of Conduct
A solid sourcing strategy begins with well defined principles that express your commitment to sustainability and ethical standards. By developing comprehensive codes of conduct, firms provide a framework for decision-making that applies to every level of the supply chain.
Conduct Rigorous Supplier Due Diligence
Performing rigorous due diligence is vital. This means examining suppliers for cost competitiveness and also reviewing their labor policies, environmental performance, and general ethical standards.
Foster Long-Term Supplier Partnerships
Ethical sourcing is a joint effort. Building long-term partnerships with suppliers that share your commitment to ethical practices is likely to lead to mutual advantages. These alliances generally result in better negotiation results, higher quality, and increased reliability.

Emerging Trends in Direct Materials Sourcing
As global markets expand, new trends are emerging that are altering how manufacturers handle direct materials procurement.
Embracing the Circular Economy
The circular economy is gaining traction as industries aim to decrease waste and enhance resource efficiency. This regenerative approach comprises designing items for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, as well as procuring materials from recycled or renewable sources. By incorporating circular economy ideas into sourcing strategies, producers may minimize dependency on virgin materials, lessen environmental impact, and build closed-loop systems that support long-term sustainability.
Aligning with Government and International Standards
Governments worldwide are increasingly concentrating on sustainable procurement strategies. Staying informed about current guidelines and matching your sourcing procedures with international standards may offer a competitive advantage. For example, engagement in public-private partnerships and utilizing government incentives may simplify the shift to more sustainable practices. We urge manufacturers to measure their efforts against worldwide best practices and explore frameworks such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to guide their activities.
Integrating Social and Economic Impact Metrics
While environmental measures have typically dominated sustainability initiatives, there is rising understanding of the need to properly quantify social and economic implications. By adopting comprehensive measurements that incorporate fair labor conditions, community development, and long-term economic benefit, firms may receive a holistic perspective of their sourcing performance.
Balancing Economic, Social, and Environmental Considerations
Manufacturers nowadays are pressed with a multidimensional challenge: cutting costs and boosting efficiency while ensuring that every component of their supply chain follows ethical standards.
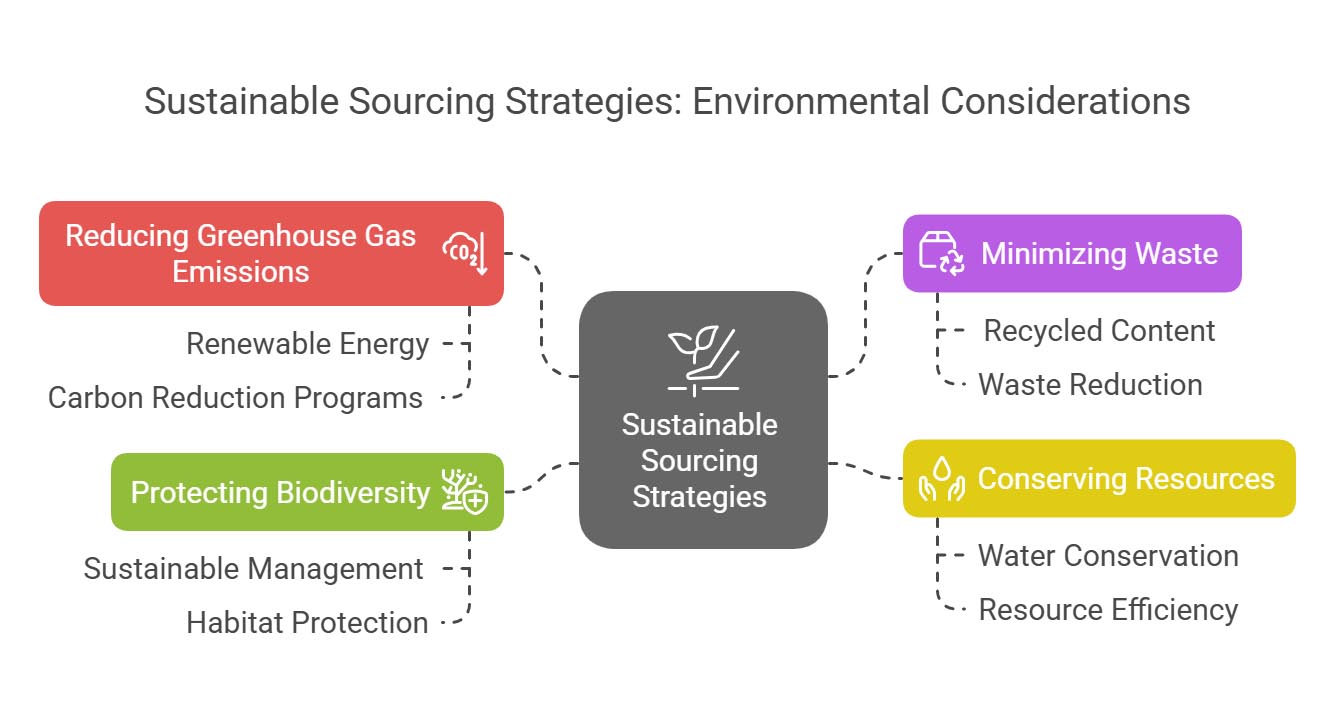
Environmental Considerations
Sustainable sourcing strategies start with a dedication to reducing environmental effect. This involves:
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Prioritizing suppliers who utilize renewable energy sources and actively promote carbon reduction programs.
Minimizing Waste: Selecting goods that integrate recycled content and stressing waste reduction across the supply chain.
Conserving Resources: Partnering with suppliers who adopt water conservation and resource efficiency strategies.
Protecting Biodiversity: Sourcing goods from suppliers who practice sustainable management of natural resources and avoid contributing to deforestation or habitat damage.
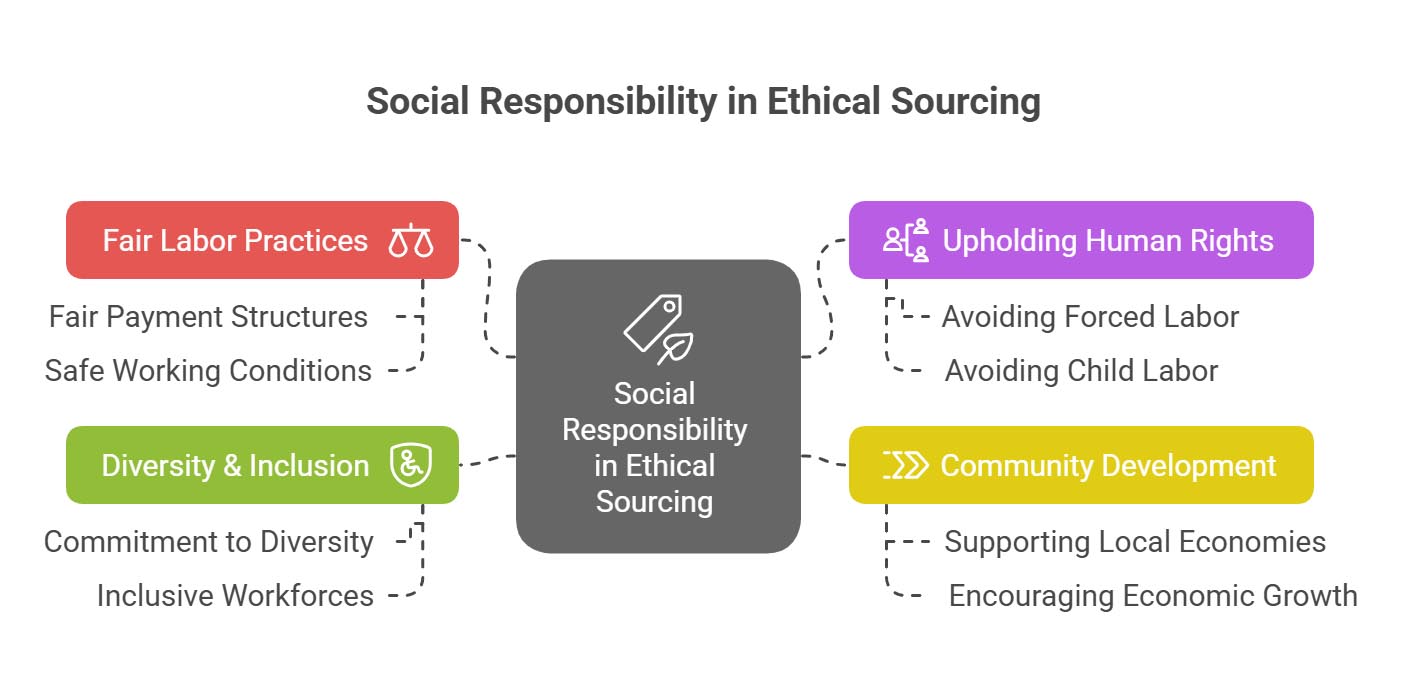
Social Considerations
Social responsibility is a vital part of ethical sourcing. Manufacturers must guarantee that their sourcing choices favorably influence the communities and workforces involved. This might include:
Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring that all suppliers conform to fair labor standards, from fair payment structures to safe working conditions.
Upholding Human Rights: Avoiding suppliers that participate in forced or child labor and ensuring that human rights are upheld at every level.
Community Development: Supporting local economies via sourcing choices that encourage economic growth and development.
Diversity & Inclusion: Giving priority to suppliers who show a commitment to diverse and inclusive workforces and processes.
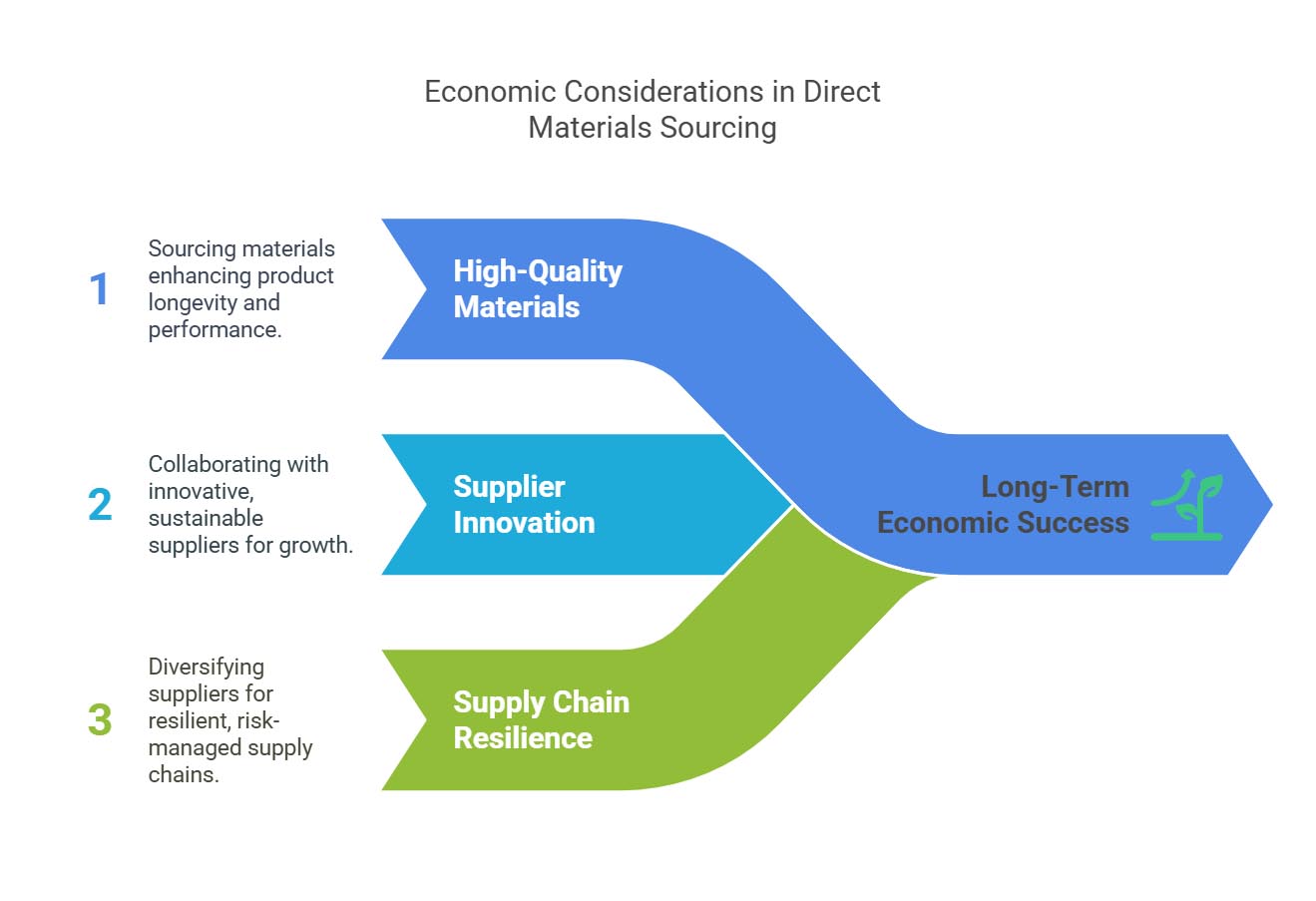
Economic Considerations
Economic considerations include:
Long-Term Value Creation: Sourcing high-quality materials that contribute to the longevity and performance of products.
Innovation: Collaborating with suppliers who are at the forefront of sustainable practices and new technologies.
Supply Chain Resilience: Diversifying sourcing options and working with suppliers who have robust risk management practices to build more resilient supply chains.
The Business Case for Ethical Direct Materials Sourcing
In recent years, the integration of sustainability and ethics into direct materials sourcing has become financially beneficial. A report by the World Economic Forum suggested that sustainable and ethical sourcing techniques may cut supply chain costs by as much as 9% to 16%, while improving revenues by up to 20% for responsible products and enhancing brand value by 15% to 30%.
Key advantages include:
Reduced Costs: Implementing sustainable practices, such as energy efficiency and waste reduction, which means considerable cost savings over time.
Improved Efficiency: Ethical sourcing reduces interruptions, allowing smoother and more predictable supply chain operations.
Enhanced Brand Reputation: With customers increasingly expecting sustainably sourced goods, a commitment to ethical standards may considerably boost a brand’s image.
Increased Sales Revenue: Manufacturers that connect with sustainable trends may tap into developing markets, drawing clients who are looking for ethical approaches.
Employee Engagement: Companies that encourage ethical sourcing tend to generate stronger employee morale and attract top talent.
Risk Mitigation: A focus on sustainability helps minimize risks, from regulatory non-compliance to reputational harm.
At Source One, we understand that direct materials sourcing is a strategic component that may revolutionize a manufacturer’s whole business.
